The two major classes of breast cancer are invasive and noninvasive. Non-invasive breast cancers stay inside the milk ducts and lobules of the breast. Invasive cancers unfold past these areas and invade standard tissue.
The main noninvasive type is ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS), in which cancer develops in the ducts that lift milk to the nipple but does no longer spread past those ducts.
A an identical condition, lobular carcinoma in situ, begins within the lobules, the milk-producing glands, and does no longer grow additional. Unlike DCIS, LCIS isn’t regarded as a most cancers, however it does imply that a girl has a higher chance of creating breast cancer.
Invasive Ductal Carcinoma: The Most Common Kind
The most commonplace form of breast cancer is invasive ductal carcinoma (IDC), infrequently often known as infiltrating ductal carcinoma. About 80 percent of all new breast cancer cases in women, and just about all breast most cancers in men, are IDC. The chance of IDC additionally will increase as other folks get older.
IDC begins within the ducts just as DCIS does, however the most cancers then grows past the ducts and invades, or infiltrates, the fatty tissue surrounding the ducts. Without treatment, the most cancers continues to metastasize, or unfold, into the lymph nodes and bloodstream.
The options to be had to treat IDC rely on the kind of breast cancer it is, what mutations it does or does no longer have, how aggressive it is, and other elements. One of an important of those other components is the most cancers stage.
Breast Cancer Stage: What do They Mean?
Stages are numbers used to explain how a long way a cancer has complex and the place it has spread within the body. Cancer that has now not unfold beyond your breast is considered native.
Regional most cancers has unfold into the breast pores and skin, chest buildings, and lymph nodes. When most cancers spreads to other portions of the frame, it is considered far-off because it exists a ways away from just the breasts.
Your prognosis, or your long-term outcome, is predicated heavily on what degree your most cancers is. Cancer phases are frequently further broken down into subcategories to provide extra particular information.
Staging previously relied handiest on if it is invasive or noninvasive, the tumor’s dimension, which lymph nodes (if any) contained most cancers, and the place and how a long way the most cancers had spread.
Breast cancer stages now also bear in mind the tumor’s grade and the cancer’s estrogen receptor, progesterone receptor, and HER2 status.
Estrogen receptor, progesterone receptor, and HER2 standing all have to do with the precise hormones and/or proteins involved for your cancer. The tumor grade describes what the cancer cells look like.
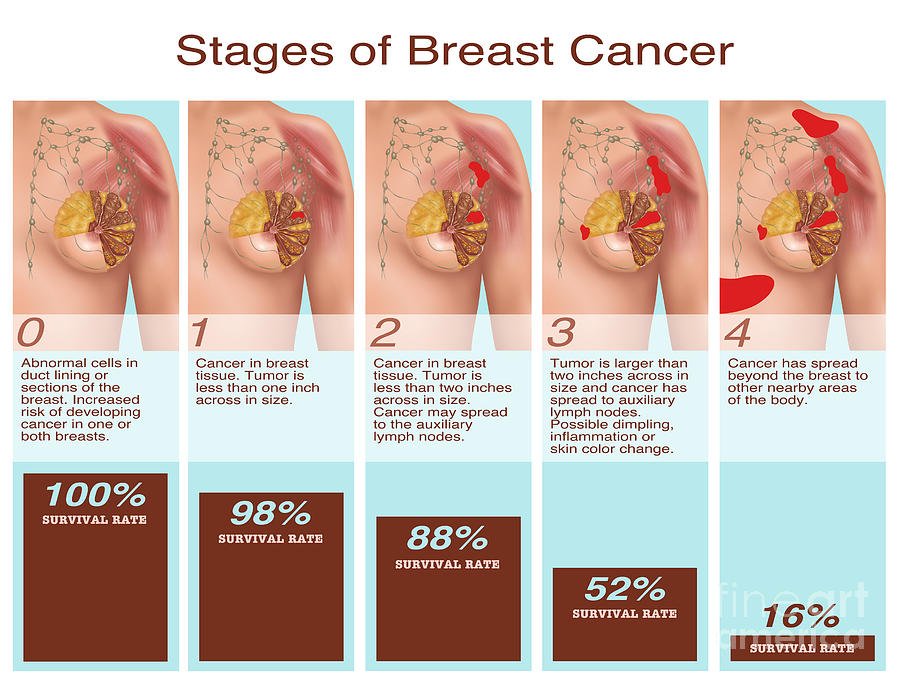
The Breast Cancer Stages: From zero to 4
The degree of your most cancers will appear to your pathology report, a file that main points the dimensions, shape and look of the cancer cells underneath a microscope. . Most cancers, including invasive breast cancer, have four stages.
Stage 0 is abnormal cells that have not spread past the ducts or lobules of the breast, akin to DCIS or LCIS, respectively.
Stage I cancer is invasive and spreading past the place it started.
In Stage IA, the cancer is two cm or smaller and has now not unfold into the lymph nodes or out of doors of the breast.
In Stage IB, small clumps of cancer cells starting from 0.2 to 2 mm exist within the lymph nodes. There is probably not a tumor within the breast, but when there’s, it measures no bigger than 2 cm.
Stage II cancer additionally has two subcategories. Stage IIA describes a cancer that has unfold to at least one to three lymph nodes underneath your arms (axillary lymph nodes) without or with a tumor as much as 2 cm large in the breast, or the breast tumor measures 2 to 5 cm with out cancer cells within the axillary lymph nodes.
Stage IIB refers to a tumor between 2 and 5 cm in conjunction with most cancers in 1 to a few axillary lymph nodes or lymph nodes near the breastbone, or the tumor is larger than five cm when no cancer cells exist in the axillary lymph nodes.
Stage III breast cancer contains Stage IIIA, IIIB, and IIIC. In degree IIIA, the tumor may be any size or may not exist in any respect. In addition, the most cancers has spread to 4 to nine lymph nodes with regards to the breastbone or within the axilla.
The tumor will also be higher than five cm with small clumps of breast most cancers cells in the lymph nodes or the tumor is larger than five cm and has spread to one to a few axillary lymph nodes or nodes close to the breast bone.
In Stage IIIB, the tumor (any measurement) has reached the outside of your breast and/or your chest wall and as much as 9 lymph nodes under your hands or close to your breastbone.
Inflammatory breast most cancers is automatically Stage IIIB or a later level.
Stage IIIC comes to three behaviors of the most cancers:
• The cancer may not be found within the breast in any respect, or may be any measurement and has spread to the chest and breast pores and skin as in level IIIB.
• 10 or more axillary lymph nodes
• The lymph nodes above or beneath your collarbone include the cancer.
• The axillary lymph nodes and the ones near your breastbone may include the most cancers.
Stage IV breast most cancers has spread beyond the breast and lymph nodes to different spaces within the body. Breast most cancers is not curable at Stage IV, but remedies can help treat it in order that a woman can live a few years while managing breast most cancers as a chronic condition.
In fact, more than 154,000 girls are estimated to be residing with level IV breast most cancers presently. About one quarter of them have been diagnosed with stage IV cancer, and the other three quarters were diagnosed with an earlier level that complicated to level IV.
Survival from or with breast most cancers has endured to increase over the past decade as rates of loss of life from the disease have fallen. Some professionals estimate that the 5-year survival charge of ladies beneath age 50 who are recognized with stage IV breast most cancers will double from 18% to 36%. (five)
Tumor Grades: How the Cells Look
The tumor grade, also known as the mobile grade, is a scale of G1 to G3 that identifies how unusual the cancer cells glance below a microscope.
Cells in grade 1 tumors glance almost customary and develop and spread slowly. Grade three cells are probably the most unusual and grow the quickest. Grade 2 cells fall between grades 1 and three.
Part of a lady’s diagnosis, or long-term end result, depends upon the cancer’s degree and the tumor’s grade. Other elements that affect prognosis come with the kind of breast cancer a lady has, the hormones or proteins concerned, and how briefly tumor cells are dividing and the tumor is growing.